When we think about the evolution of technology, one of the most fascinating journeys is that of data storage. Hard disks have played a pivotal role in this evolution, transitioning from bulky, limited-capacity devices to sleek, high-speed storage solutions. Let’s take a look at how hard disks have evolved over the years and what the future holds for secondary storage media.
The Beginnings: Magnetic Disks
The history of hard disks commenced in 1956 with IBM’s unveiling of the IBM 350 Disk File, which was an integral component of the IBM 305 RAMAC system. This pioneering hard disk storage system utilized an array of 50 platters, each measuring 24 inches in diameter, to store an impressive 5 MB of data. Although this may appear negligible by modern standards, it was a revolutionary achievement at the time. The disk boasted a data transfer rate of approximately 8,800 characters per second, a remarkable advancement that met the data processing requirements of that era.

IBM 350 RAMAC, capacity 5Mb, that is being restored by volunteers in the en: Computer History Museum in Mountain View, CA.
Credit to the original Owner
The Rise of Portable Storage
The 1980s heralded the dawn of personal computing, accompanied by a growing demand for storage solutions that were both more compact and cost-effective. During this transformative era, innovative companies like Seagate introduced the 3.5-inch hard disk drive to the market. These drives provided enhanced storage capacity, with some models capable of holding up to 10 MB of data, establishing themselves as the standard for personal computers. Their reduced physical size and lower cost made them increasingly accessible to a wider audience, significantly contributing to the widespread adoption of personal computing technology.
The ST-506 and ST-412 (sometimes written ST506 and ST412) were early hard disk drive products introduced by Seagate in 1980 and 1981 respectively, that later became construed as hard disk drive interfaces: the ST-506 disk interface and the ST-412 disk interface. Introduced in 1980, the ST-506 was the first 5.25 inch HDD. Its successor, the ST-412, was introduced in 1981 and implemented a refinement to the seek speed, and increased the drive capacity from 5 MB to 10 MB, but was otherwise highly similar
wikipedia.org

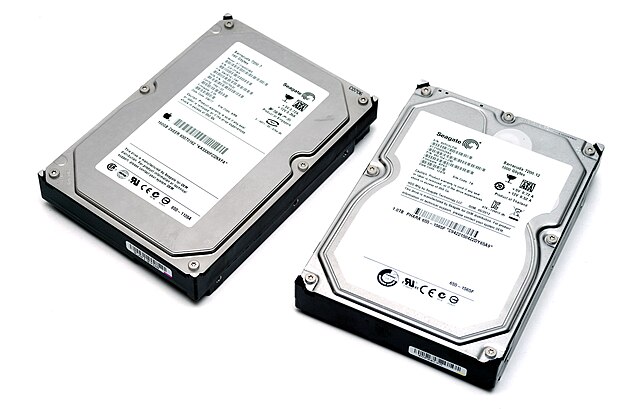
The Era of Personal Computing
The 1980s witnessed the explosion of the personal computer onto desktops in homes and offices. This shift demanded storage solutions that could be integrated directly into these new machines. The introduction of the 3.5-inch hard disk drive by companies like Seagate was a pivotal moment. These drives, offering capacities up to 10 MB—a significant leap at the time—became the de facto standard for desktop computers. Crucially, this increased storage capacity fueled the development of more complex software applications, from word processors and spreadsheets to early graphical user interfaces, paving the way for the modern software landscape. The smaller form factor also allowed for more compact computer designs, further solidifying the PC’s place on the desktop.

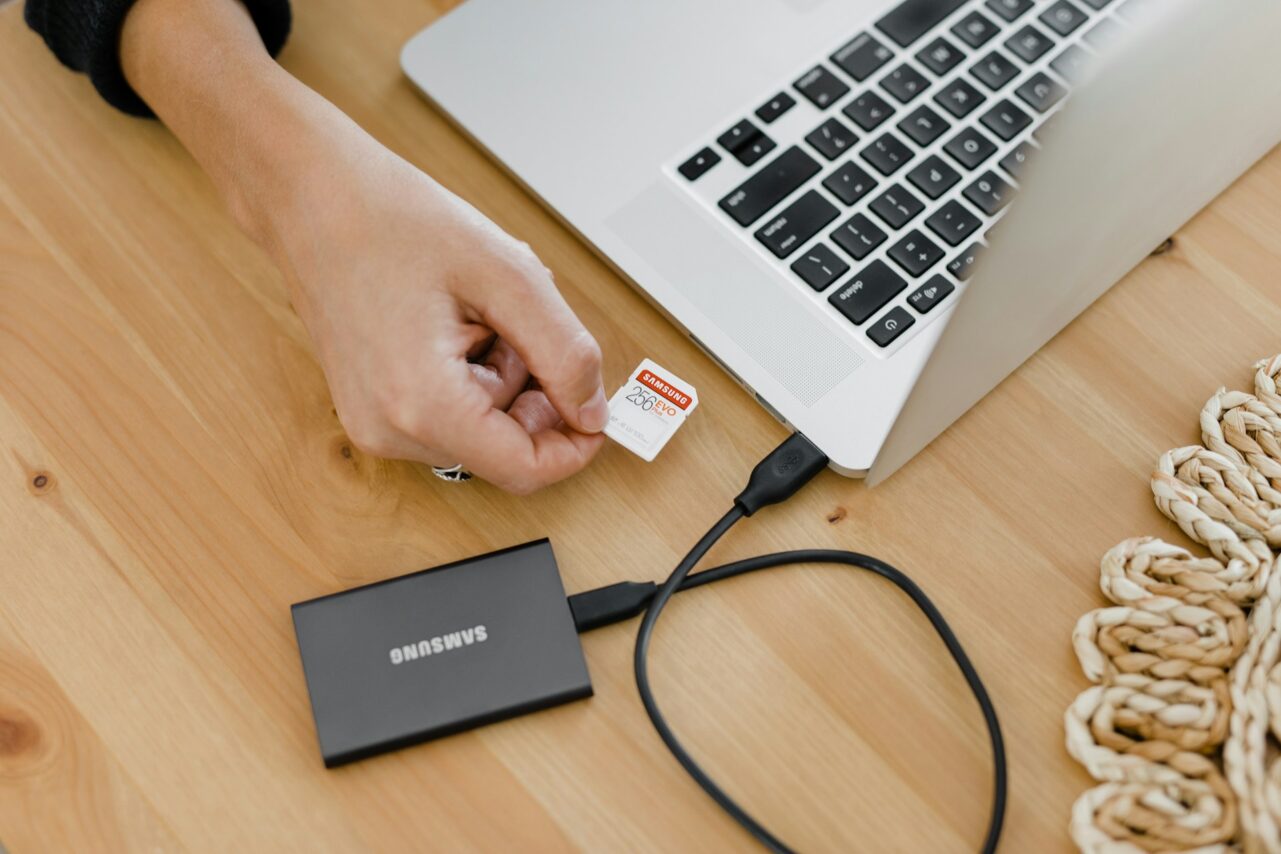
The Transition to Digital: SSDs and Beyond
The 21st century has witnessed a significant transition from conventional spinning disk hard drives (HDDs) to the more advanced solid-state drives (SSDs). These SSDs utilize flash memory for data storage, providing numerous benefits over HDDs. They deliver much faster data access speeds, consume less power, and are more durable because they have no moving parts. As the costs of SSDs have fallen, they have increasingly become a standard choice in both personal and enterprise settings, gaining widespread adoption across various applications.

The Future of Storage: Cloud and Beyond
Today, SSDs are advancing rapidly, especially with innovations such as NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) that significantly enhance speed and overall performance. However, the horizon of storage technology is expanding beyond these developments, with a substantial focus on cloud storage. Cloud storage solutions deliver almost limitless storage capacity and the ease of accessing data from any location with an internet connection. Major companies such as Google, Amazon, and Microsoft are at the forefront, offering comprehensive and reliable cloud storage services tailored for both personal and business needs. These services are reshaping how data is managed, stored, and accessed on a global scale.

Conclusion
From the enormous disk files of the 1950s to the sleek solid-state drives (SSDs) and expansive cloud storage solutions available today, the evolution of hard disks highlights the rapid advancement of technology. As we continue to generate and capture vast amounts of data, the demand for cutting-edge storage solutions is set to rise, propelling further innovation in this dynamic sector. Whether through faster and more reliable local storage options or expansive and easily accessible cloud solutions, the future of data storage appears promising and limitless.


